Analysis of Polyphyllin II alters microRNA expression profile in lung cancer A549 cells
Abstract
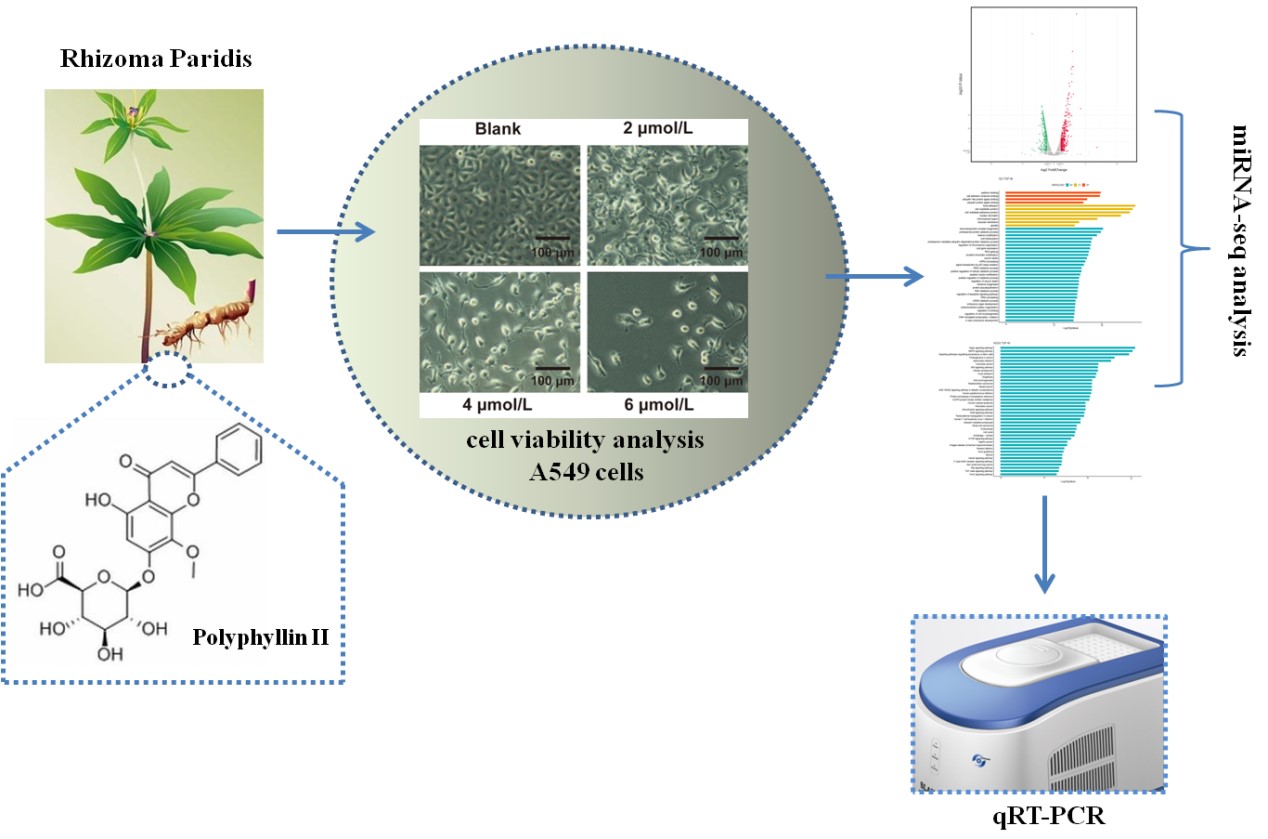
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a malignant tumor that threatens the whole world, previous studies found that Polyphyllin II (PPII) can suppress NSCLC cells growth, exhibits significant antitumor activity. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) can regulate the expression of other genes and play a crucial role in the prevention and development of cancer. However, the miRNA portrait of ginsenoside PPII-treated NSCLC A549 cells has not yet been studied. In this work, miRNA-seq analysis was used to determine the changes in miRNA expression profile of NSCLC A549 cells PPII-treaded. In addition, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis were performed on differentially expressed miRNA target genes. Then, predicted the target genes of miRNA and performed functional enrichment analysis on them. We identified 58 up-regulated and 24 down-regulated miRNAs displaying changes their expression in PPII treated A549 cells were greater than 2-fold. In addition, the expression levels of miRNAs were validated by real-time PCR. Therefore, this work has a certain promoting effect on the study of the anti-cancer mechanism of PPII in lung cells.
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2022; 72(1): 7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708
2. Bodor JN, Boumber Y, Borghaei H. Biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibition in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cancer. 2019; 126(2): 260-270. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32468
3. Alduais Y, Zhang H, Fan F, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A review of risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Medicine. 2023; 102(8): e32899. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000032899
4. Giroux DJ, Van Schil P, Asamura H, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: A Renewed Call to Participation. Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 2018; 13(6): 801-809. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.02.012
5. Wang CY, Huang HS, Su YC, et al. Conventional treatment integrated with Chinese herbal medicine improves the survival rate of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 2018; 40: 29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2018.07.003
6. Huang N, He H, He Y, et al. Xiaotan Sanjie recipe, a compound Chinese herbal medicine, inhibits gastric cancer metastasis by regulating GnT-V-mediated E-cadherin glycosylation. Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2023; 21(6): 561-574. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2023.11.001
7. Jiang L, Kang LP, Liu DH, et al. Herbal textual research on origins of Chonglou. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017; 42: 3469-3473. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2017.0134
8. Zhao F, Zhao P, Chang J, et al. Identification and vitro verification of the potential drug targets of active ingredients of Chonglou in the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma based on EMT-related genes. Frontiers in Genetics. 2023; 14. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1112671.
9. Li J, Jia J, Zhu W, et al. Therapeutic effects on cancer of the active ingredients in rhizoma paridis. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2023; 14. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1095786
10. Zhou D, Pan QD, Yan XX, et al. Research progress of steroidal saponins in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis and their microbial transformation. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022; 47: 4863-4876. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220506.204
11. Xu XH, Li T, Fong C, et al. Saponins from Chinese Medicines as Anticancer Agents. Molecules. 2016; 21(10): 1326. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101326
12. Luo Q, Jia L, Huang C, et al. Polyphyllin I Promotes Autophagic Cell Death and Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells via the ROS-Inhibited AKT/mTOR Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16): 9368. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169368
13. Gardiner P, Cox RJ, Grime K. Plasma Protein Binding as an Optimizable Parameter for Acidic Drugs. Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 2019; 47(8): 865-873. doi: 10.1124/dmd.119.087163
14. You L, Geng H, Yang X, et al. The comparison analysis of polyphyllin I and its analogues induced apoptosis of colon and lung cancer cells via mitochondrial dysfunction. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology. 2021; 129(1): 15-25. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13596
15. Hatam S. MicroRNAs Improve Cancer Treatment Outcomes Through Personalized Medicine. MicroRNA. 2023; 12(2): 92-98. doi: 10.2174/2211536612666230202113415
16. Liu P, Yang X, Zhang H, et al. Analysis of change in microRNA expression profiles of lung cancer A549 cells treated with Radix tetrastigma hemsleyani flavonoids. OncoTargets and Therapy. 2018; 11: 4283-4300. doi: 10.2147/ott.s164276
17. Xu D, Chi G, Zhao C, et al. Ligustrazine Inhibits Growth, Migration and Invasion of Medulloblastoma Daoy Cells by Up-Regulation of miR-211. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2018; 49(5): 2012-2021. doi: 10.1159/000493712
18. JIN H, QIAO F, WANG Y, et al. Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer cells through the upregulation of miR-192-5p and suppression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncology Reports. 2015; 34(5): 2782-2789. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4258
19. Xu F, Li Q, Wang Z, et al. RETRACTED: Sinomenine inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and promotes apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by regulation of miR-23a. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2019; 112: 108592. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.01.053
20. Liang HX, Sun LB, Liu NJ. RETRACTED: Neferine inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of U251 glioma cells by down-regulation of miR-10b. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2019; 109: 1032-1040. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.122
21. Yuan L, Miao H, Ding H, et al. Polyphyllin I suppressed the apoptosis of intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cells induced by IL-1β by miR-503-5p/Bcl-2 axis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. 2023; 18(1). doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03947-7
22. Niu W, Xu L, Li J, et al. Polyphyllin II inhibits human bladder cancer migration and invasion by regulating EMT‑associated factors and MMPs. Oncology Letters. 2020; 20(3): 2928-2936. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11839
23. Pang D, Yang C, Li C, et al. Polyphyllin II inhibits liver cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion through downregulated cofilin activity and the AKT/NF-κB pathway. Biology Open. 2020; 9(2). doi: 10.1242/bio.046854
24. Azlan A, Rajasegaran Y, Kang Zi K, et al. Elucidating miRNA Function in Cancer Biology via the Molecular Genetics’ Toolbox. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(4): 915. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040915
25. Ramelli SC, Gerthoffer WT. MicroRNA Targets for Asthma Therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021; 1303: 89-105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-63046-1_6
26. Wang Y, Xu X, Maglic D, et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of the Hippo Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Cell Reports. 2018; 25(5): 1304-1317.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.001
27. Park HB, Baek KH. E3 ligases and deubiquitinating enzymes regulating the MAPK signaling pathway in cancers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer. 2022; 1877(3): 188736. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188736
28. Slattery ML, Mullany LE, Sakoda LC, et al. The MAPK-Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer: Dysregulated Genes and Their Association with MicroRNAs. Cancer Informatics. 2018; 17. doi: 10.1177/1176935118766522
29. Gao C, Wang B, Chen Q, et al. Serum exosomes from diabetic kidney disease patients promote pyroptosis and oxidative stress through the miR-4449/HIC1 pathway. Nutrition & Diabetes. 2021; 11(1). doi: 10.1038/s41387-021-00175-y
30. Zhao Q, Li B, Zhang X, et al. M2 macrophage-derived lncRNA NORAD in EVs promotes NSCLC progression via miR-520g-3p/SMIM22/GALE axis. npj Precision Oncology. 2024; 8(1). doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00675-x
31. Maurel M, Jalvy S, Ladeiro Y, et al. A functional screening identifies five micrornas controlling glypican-3: role of mir-1271 down-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2013; 57(1): 195-204. doi: 10.1002/hep.25994
32. Park EG, Lee DH, Kim WR, et al. Human Endogenous Retrovirus-H-Derived miR-4454 Inhibits the Expression of DNAJB4 and SASH1 in Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Genes. 2023; 14(7): 1410. doi: 10.3390/genes14071410
33. Wang H, Hu H, Luo Z, et al. miR-4454 up-regulated by HPV16 E6/E7 promotes invasion and migration by targeting ABHD2/NUDT21 in cervical cancer. Bioscience Reports. 2020; 40(9). doi: 10.1042/bsr20200796
34. Kannathasan T, Kuo WW, Chen MC, et al. Chemoresistance-Associated Silencing of miR-4454 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Aggression through the GNL3L and NF-κB Pathway. Cancers. 2020; 12(5): 1231. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051231
35. Feng L, Feng Z, Hu J, et al. Identification of hsa-miR-619-5p and hsa-miR-4454 in plasma-derived exosomes as a potential biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma. Frontiers in Genetics. 2023; 14. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1138230
36. Dasari S, Pandhiri T, Grassi T, et al. Signals from the Metastatic Niche Regulate Early and Advanced Ovarian Cancer Metastasis through miR-4454 Downregulation. Molecular Cancer Research. 2020; 18(8): 1202-1217. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-19-1162
37. Hill M, Tran N. miRNA interplay: mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Disease Models & Mechanisms. 2021; 14(4). doi: 10.1242/dmm.047662
Copyright (c) 2024 Weidong Peng, Huimin Huang, Jingjian Liu, Binqiang Zhang, Lun Wu, Zhongzhi Liu, Fengying Ran

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright on all articles published in this journal is retained by the author(s), while the author(s) grant the publisher as the original publisher to publish the article.
Articles published in this journal are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International, which means they can be shared, adapted and distributed provided that the original published version is cited.



 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper
